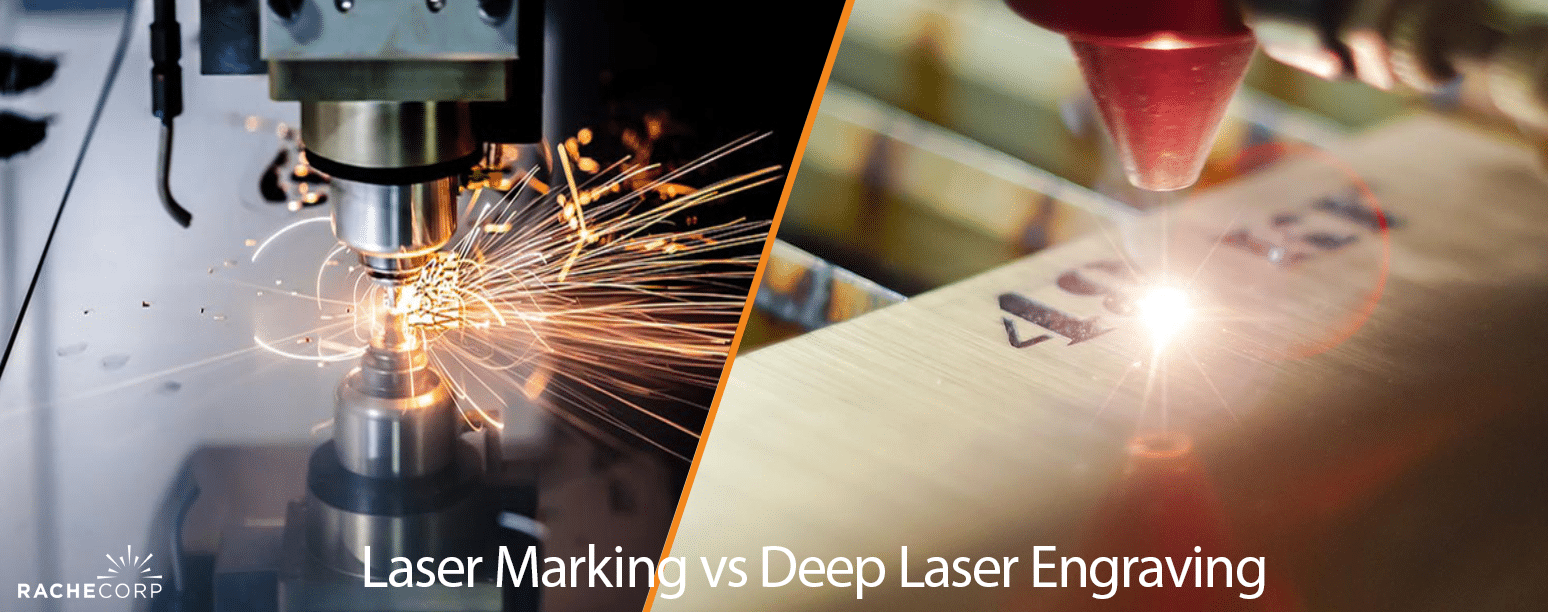
Every manufacturer knows the importance of permanent marks. A code that fades or a logo that wears off can create serious problems like lost traceability, failed inspections, or expensive rework. The challenge is knowing which process to trust for your parts.
Many companies get stuck choosing between laser marking and deep laser engraving. On the surface, they sound alike. Both use lasers, both create permanent results, and both are widely used in industry. But they are not the same. Picking the wrong method can cost you money and even compromise product reliability.
The key is knowing how the two processes differ and where each works best. Once you understand the technical details, materials, and industries they serve, the choice becomes clear.
Also Read: Traceability Made Easy: Why Manufacturers Choose Laser Marking Over Labels
Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics of Laser Material Processing
Before we dive into comparisons, it helps to define what each process actually does.
What Is Laser Marking?
Laser marking is when a laser changes the surface of a material without really cutting into it. It just hits the top layer, kind of heating or shifting it, and that creates contrast. The result is a clear mark you can actually see, like a logo, barcode, or serial number sitting right on the surface.
It’s quick, it’s accurate, and that’s why a lot of companies use it when they’ve got to mark a bunch of parts. You’ll notice it on electronics, medical tools, or even those anodized aluminum cases. The best part is it doesn’t mess with the material itself, so the part stays intact. That’s really important if you’re dealing with small or delicate stuff that can’t be damaged.
What Is Deep Laser Engraving?
Deep laser engraving is basically when the laser goes past the surface and actually cuts into the material. Instead of just making a light mark, it removes layers and carves into the part. How deep it goes depends on what you need. Sometimes it’s only a small cut, other times it can be a few millimeters deep.
The cool thing is these marks aren’t just something you look at, you can actually feel them with your finger. It does take more time compared to laser marking, but the payoff is big because the mark doesn’t wear away. It holds up against scratches, constant use, and even really harsh conditions.
That’s why you’ll see deep engraving on aerospace parts, auto tools, and heavy-duty equipment. Those parts take a beating, and the marks have to last for years without fading.
Technical Differences Between Marking and Engraving
Laser marking and engraving use similar technology but behave differently once applied.
Depth of Material Alteration
Marking works on the surface at a microscopic level. It doesn’t dig into the material, so it’s quick and produces high contrast. Engraving removes more material, giving you a permanent, tactile mark.
Equipment and Laser Power Requirements
Marking usually needs lower or medium power lasers, while engraving demands higher power and longer processing times. Engraving equipment often includes extra controls for precision since the process must go deeper without damaging the part.
Speed and Processing Time
Marking wins when speed matters. It can handle thousands of parts per hour. Engraving is slower, but the tradeoff is permanence. If durability is the top priority, time becomes a secondary concern.
Materials Best Suited for Each Technique
Different materials respond better to marking or engraving.
Laser Marking Materials
Laser marking is well-suited for:
- Plastics
- Coated metals
- Anodized aluminum.
- Painted surfaces
These materials don’t need deep cuts. A contrast mark is enough for traceability or branding. For example, a QR code on a plastic part doesn’t need to be deep, only readable.
Deep Laser Engraving Materials
Deep engraving works best on:
- Stainless steel
- Titanium
- Hardened alloys
- Industrial tools and dies
These are tougher materials that often face abrasion, harsh cleaning chemicals, or weather exposure. Engraving ensures the mark stays clear no matter the conditions.
Durability and Longevity of Marks
The life span of a mark depends on the process chosen.
How Laser Marking Holds Up Over Time
Laser marking is reliable under normal conditions. Marks hold up well on electronics, consumer products, or coated surfaces. However, in abrasive or high-contact environments, the marks may eventually fade.
Why Deep Laser Engraving Lasts Longer
Deep engraving is practically permanent. Even if the surface gets scratched or worn, the engraved mark remains visible. This is why industries like aerospace, defense, and medical devices rely on it. For them, losing traceability is not an option.
Application Areas Across Industries
Both laser marking and deep laser engraving are important, but the industry often decides which one makes the most sense.
Industrial Traceability and Compliance
Laser marking is used all the time for barcodes, serial numbers, and QR codes. These marks are what keep products traceable through the supply chain and make sure they meet compliance standards. Deep engraving comes in when the rules require marks that stick around for the entire life of the part.
Branding and Aesthetics for Ecommerce
Marking works great for logos, product names, or other branding on the surface. It gives you sharp contrast while leaving the feel of the material the same. Engraving is a different story. It’s chosen when brands want a bold, tactile look, like on tools, watches, or high-end goods where the depth makes the logo feel premium.
Safety-Critical and High-Stress Environments
In aerospace, defense, and automotive, deep engraving is standard. These parts face extreme conditions and need permanent identification. Marking still plays a role in electronics, packaging, and consumer goods where exposure is less demanding.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Both processes come with different price points and returns.
- Laser Marking: Lower upfront cost, quicker cycle times, and lower operating expenses. Best for high-volume production where speed and clarity matter.
- Deep Laser Engraving: Higher upfront cost, slower process, but longer-lasting results. Best for parts where durability saves money in the long run.
Here’s a side-by-side look to make the differences easier to see:
| Factor | Laser Marking | Deep Laser Engraving |
| Depth | Microns (surface only) | Millimeters (carved in) |
| Speed | Fast, high-volume | Slower, more detailed |
| Durability | Strong in normal use | Extreme, long-lasting |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Higher upfront |
| Best For | Barcodes, logos, consumer goods | Aerospace, tools, medical parts |
Also Read: Complete Guide to Laser Solutions for the Industrial Sector
Common Misconceptions About Marking and Engraving
A few myths keep circulating about these processes.
“Laser Marking Is Too Weak for Industrial Use”
This isn’t true. Marking is widely used in electronics, packaging, and compliance coding. It’s reliable, just not built for extreme wear.
“Deep Engraving Always Damages the Part”
Done correctly, deep engraving does not weaken a part. Skilled operators and advanced equipment make sure the engraving adds permanence without compromising strength.
“Both Processes Are Basically the Same”
They may look similar from the outside, but they serve different needs. Speed, depth, and durability are not interchangeable.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Needs
It comes down to what you need most.
Key Questions to Ask
- Do you need speed or permanence?
- Is surface contrast enough?
- Will the part face extreme wear or chemicals?
Matching Process to Application
Laser marking works best for consumer products, electronics, and branding. Deep engraving is essential for aerospace, defense, medical devices, and tools where marks must survive harsh conditions.
Working With Experts to Decide
It’s not always an easy choice, which is why working with experienced providers matters. At Rache Corp, we test and advise so clients don’t waste time or money guessing.
The Future of Permanent Marking Technologies
Lasers are becoming smarter and greener. Machine-readable marks like QR codes are now being paired with digital traceability systems. This makes supply chains easier to track and ensures compliance.
On the sustainability side, lasers are cleaner than ink or labels since they don’t create waste. That makes them a strong choice for companies focused on reducing environmental impact.
Conclusion
Laser marking and deep laser engraving both have their place. Marking is quick and great for codes, logos, and everyday branding. Engraving takes longer but gives you depth and permanence that critical parts need. The choice really comes down to how the part will be used and what kind of conditions it has to handle.
At Rache Corp, we’ve been working with lasers for over 30 years. We’ve done cutting, welding, marking, and everything in between. Our job is to help you figure out the right process without wasting time on trial and error. If you’re looking at a project and need some guidance, give us a call at (805) 389-6868. We’ll talk it through and find the best solution for you.
FAQs
Is laser marking cheaper than deep engraving?
Yes, marking is usually cheaper because it uses less power and takes less time. Engraving costs more upfront but can save money in the long run since the marks never fade.
Can you mark and engrave the same part?
Yes. Some companies use marking for traceability codes and engraving for permanent IDs on the same piece.
Do both methods work on plastics?
Laser marking works well on plastics. Deep engraving usually does not, since plastics can warp or burn under high power.
Which industries depend most on deep engraving?
Aerospace, defense, medical devices, and automotive are the biggest users because they need marks that survive the toughest conditions.